Understanding Duties, Preferences, and Free Trade Agreements for Smarter Market Entry
Introduction: Japan’s Trade and Tariff Landscape

Tariffs are the customs duties levied on imported goods, as specified by the importing country’s government. In essence, a tariff is a tax on imports, generating revenue for the government while also serving as a policy tool. Traditionally, tariffs are applied as a form of import substitution to encourage domestic production of targeted goods. Under the World Trade Organization (WTO), most countries follow the Most Favoured Nation (MFN) principle, which promotes fairness and non-discrimination in global trade relationships.
Against this global backdrop, Japan’s customs regime plays a defining role for businesses seeking market entry. In Japan, tariffs are not merely taxes on imports—they function both as a revenue source and as a safeguard for domestic industries. For international companies, understanding how Japan applies tariffs, exemptions, and preferential agreements is essential for building a successful entry strategy.
This article breaks down Japan’s customs system, highlighting the structure of tariffs, special preferential schemes, and the role of major free trade agreements (FTAs) in shaping access to the Japanese market.
Types of Customs Duties in Japan
Japan imposes tariffs across a broad spectrum of imports—from agricultural products and textiles to machinery and transport equipment. Three core duty rates apply:
- General rate: Based on the Customs Tariff Act
- Temporary rate: Applied to specific goods for a fixed period
- WTO tariff treaty rate: Derived from Japan’s obligations under the World Trade Organization.
To ease the burden on smaller transactions, goods with a taxable value under JPY 100,000 (USD 680) are generally exempt from duty. Imports valued at up to JPY 200,000 (USD 1,361) may qualify for a simplified rate, although exceptions exist.
Special Tariff Programs: Opportunities for Lower Duties
Japan also provides tariff reductions or exemptions under specific preferential schemes, which can significantly lower costs for eligible importers:
- Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA) rates
Tariffs are reduced or eliminated under bilateral and multilateral EPAs. Eligibility depends on the agreement’s rules of origin and other conditions. - Generalized System of Preferences (GSP)
Certain goods from developing countries benefit from lower-than-standard rates, implemented under temporary customs measures. - Least Developed Countries (LDC) preferences
Imports from designated LDCs are often zero-rated, provided they meet cabinet-specified requirements.
For companies sourcing from multiple regions, strategically leveraging these frameworks can lead to substantial savings. To make full use of such benefits, however, businesses must also comply with Japan’s customs procedures, which govern how tariffs are determined and applied in practice.
Importers must notify Japan Customs when bringing in goods subject to declaration and duty payments. In cases where tariff classification, origin, or rate is unclear, an advance ruling can be sought for clarity.
Japan’s Free Trade Agreements: Expanding Access
Japan is an active participant in several major trade agreements that reshape tariff structures and streamline customs procedures.
Table: Key Free Trade Agreements Involving Japan.
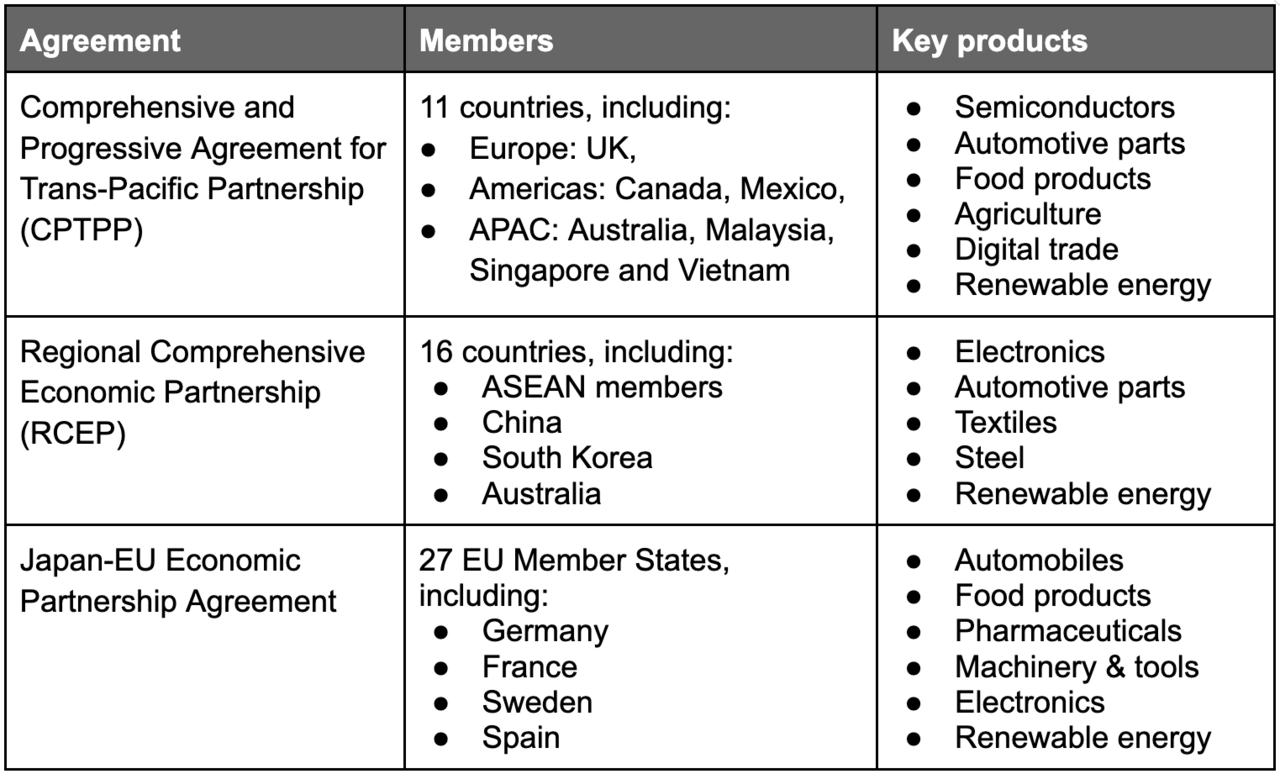
Beyond tariff reductions, these agreements provide clarity on rules of origin, simplify documentation, encourage cross-border investment, and promote digital trade—helping businesses operate more efficiently across borders.
Conclusion: Turning Complexity into Opportunity with EXPACT
Japan’s customs framework may appear complex at first glance, but it offers multiple pathways for reducing trade barriers and entering one of the world’s most attractive markets. Companies that understand how to navigate tariff structures, preferential schemes, and free trade agreements can secure a competitive edge when expanding into Japan.
This is where EXPACT Inc. comes in. As a trusted local partner, EXPACT helps global startups and investors translate regulatory challenges into actionable strategies. Through our “Soft Landing” program, we provide end-to-end support—from tariff classification and FTA utilization to market entry planning, financial advisory, and local partnerships.
By combining regulatory expertise with on-the-ground support, EXPACT empowers international businesses to turn Japan’s customs complexity into a strategic growth opportunity.
About EXPACT
EXPACT provides a variety of operational support to domestic and international startups.
EXPACT offers market entry strategy advisory for international businesses looking to establish a presence in Japan. Our services are as follows:
– Advice for visas and programs: Providing guidance on suitable visas and government programs for foreign entrepreneurs (e.g., Startup visa).
– Market research assistance: Evaluating the potential market size and demand for the product or service.
– Geographical evaluation based on the company’s target: Carrying out a location analysis to determine the most suitable region, prefecture, and city according to the startup’s specific needs.
– Support for applying for financial aid programs: Sourcing and supporting the application process for applicable government grants and subsidies.
– Assistance for forming partnerships: Serving as a liaison to help the startup establish connections with local partners, investors, and government institutions.
– Advice for a business plan: Offering a business plan review with insights from a Japanese perspective.
– Translation services: Providing translation services for in-person meetings, virtual discussions, and document preparation.
Additionally, the company also offers One-Stop support from Startup advisory to Finance, PR, Recruitment and EXIT.
- Finance and Fundraising: Advisory on the financial health of startups and proposing an optimal fundraising plan by applying for government grants and facilitating investor introductions. Activities include drafting a pitch deck, and forming a business plan and/or cap table.
- Promotion: Publishing press releases, building media relations, branding.
- Startup Advisory: Business ideation, researching, conducting interviews, MVP analysis, investment access.
- Human Resources: Personnel strategy, hiring support, institution building.
- EXIT: IPO support, M&A support, exit system design.
For assistance or additional information, please contact us at info@expact.jp for inquiries.
Inquiries on market entry strategies can be directed to pramod@expact.jp
Written by Pramod Sharma & Hana Miyagi
